Imagine this: You’re cooking dinner, and your hands are covered in flour. You need to know how long to bake a chicken, so you shout, “Hey Google, how long should I bake chicken at 375°F?” Within seconds, you have your answer. This is the power of voice search—a technology that’s changing how people find information online.
Voice search isn’t just a trend; it’s becoming a dominant way people interact with the internet. In 2025, the speech recognition market is expected to grow to a size of US$304.70 million.
For businesses, this means one thing: If you’re not optimising for voice search, you’re missing out on a massive opportunity. In this blog, we’ll break down everything you need to know about voice search optimisation, from actionable strategies to SEO tips that will help you stay ahead of the competition.
What is Voice Search Optimisation?
Voice search optimisation is the process of tailoring your website and content to rank well for voice-based queries. Unlike traditional text searches, voice searches are often longer, more conversational, and question-based. For example:
- Text Search: “best pizza near me”
- Voice Search: “Where can I find the best pizza near me that’s open now?”
To optimise for voice search, you need to understand how people speak, not just how they type.
How Does Voice Search Work?
Voice search relies on natural language processing (NLP) and artificial intelligence (AI) to understand and respond to user queries. Here’s a quick breakdown:
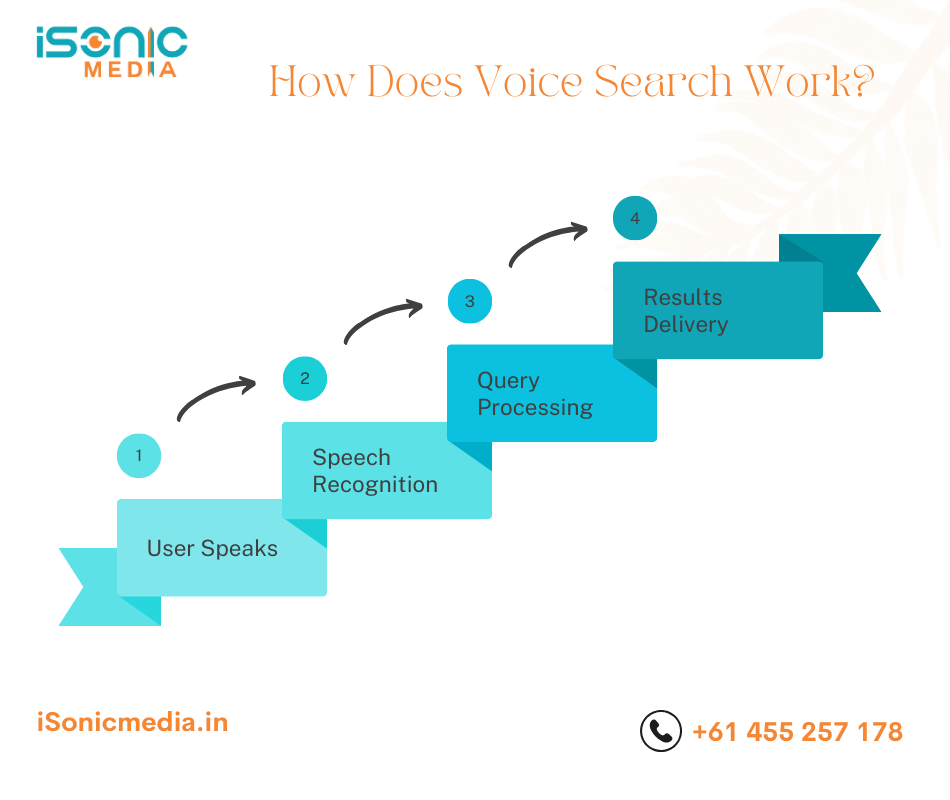
- User Speaks: The user asks a question or gives a command using a voice assistant like Siri, Alexa, or Google Assistant.
- Speech Recognition: The voice assistant converts the spoken words into text.
- Query Processing: The AI analyses the text to understand the intent behind the query.
- Results Delivery: The assistant provides a spoken or displayed answer, often pulling information from featured snippets or high-ranking websites.
Why is Voice Search Optimisation Important?
- Rising Popularity: Over 50% of adults use voice search daily.
- Local SEO Boost: 46% of voice search users look for local businesses.
- Mobile-First Indexing: Google prioritises mobile-friendly sites, which are crucial for voice search.
- Competitive Edge: Early adopters of voice search optimisation gain a significant advantage.
10 Essential Voice Search Optimisation Strategies
1. Focus on Conversational Keywords
Voice searches are more conversational than text searches. Use long-tail keywords that mimic how people speak. For example:
- Instead of “best SEO agency,” target “What is the best SEO agency near me?”
Pro Tip: Use tools like AnswerThePublic to find question-based keywords.
2. Optimise for Featured Snippets
Voice assistants often pull answers from featured snippets (the “position zero” in search results). To optimise for snippets:
- Provide clear, concise answers to common questions.
- Use headers (H2, H3) to structure your content.
- Include lists, tables, and bullet points.
Example: If you’re targeting “How to optimise for voice search,” create a section with step-by-step instructions.
3. Improve Website Speed
Voice search users expect quick answers. If your site takes too long to load, you’ll lose out.
- Use tools like Google PageSpeed Insights to test your site speed.
- Compress images and enable browser caching.
4. Make Your Site Mobile-Friendly
Over 60% of voice searches happen on mobile devices. Ensure your site is responsive and easy to navigate on smaller screens.
5. Leverage Local SEO
Voice searches often include local intent, like “near me” queries. Optimise your Google My Business profile and include local keywords in your content.
Learn more about our local SEO at our Search Sensei page.
6. Use Structured Data Markup
Structured data helps search engines understand your content better. Use schema markup to highlight key information like business hours, reviews, and FAQs.
7. Create FAQ Pages
FAQ pages are perfect for voice search optimisation because they directly answer common questions.
Example:
- Question: “What is the best time to post on social media?”
- Answer: “The best time to post on social media varies by platform, but generally, weekdays between 9 AM and 12 PM work best.”
8. Write in a Natural, Conversational Tone
Avoid overly formal language. Write as if you’re talking to a friend.
9. Optimise for Long-Tail Keywords
Long-tail keywords are more specific and less competitive. They also match the way people speak during voice searches.
10. Monitor and Adapt
Voice search trends are constantly evolving. Use tools like Google Analytics and SEMrush to track your performance and adjust your strategy.
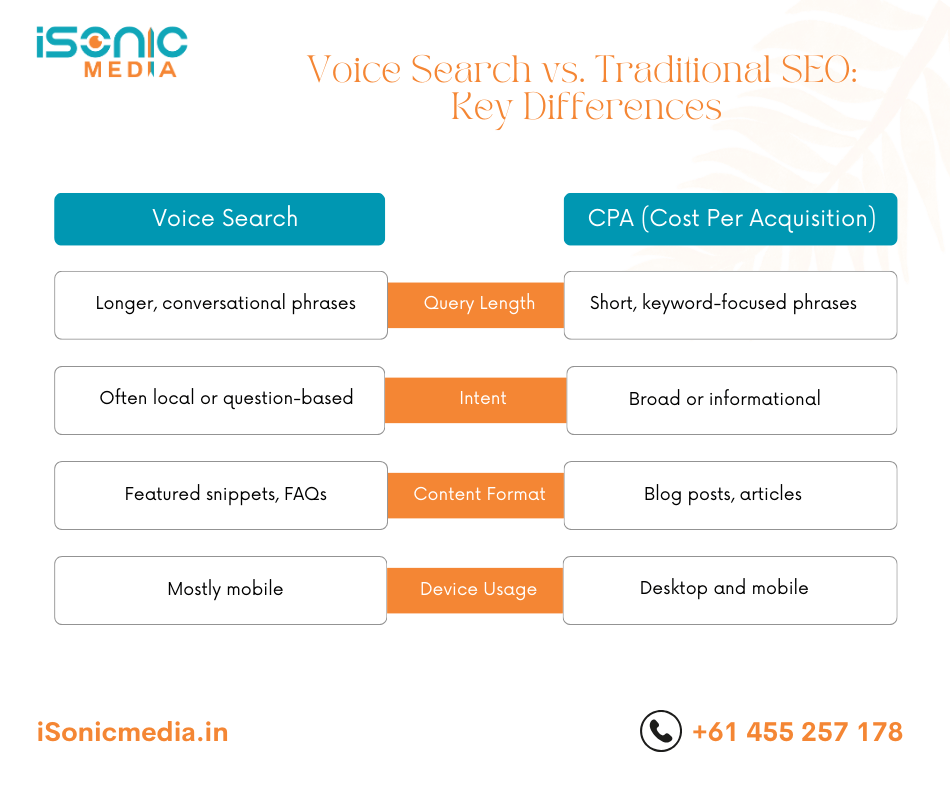
Voice Search vs. Traditional SEO: Key Differences
| Aspect | Voice Search | Traditional SEO |
| Query Length | Longer, conversational phrases | Short, keyword-focused phrases |
| Intent | Often local or question-based | Broad or informational |
| Content Format | Featured snippets, FAQs | Blog posts, articles |
| Device Usage | Mostly mobile | Desktop and mobile |
FAQs About Voice Search Optimisation
Can voice search optimisation improve my local business visibility?
Absolutely! Voice search is heavily used for local queries like “restaurants near me” or “plumbers in [city].” Optimising for local SEO can significantly boost your visibility.
How do I find the right keywords for voice search?
Use tools like Google’s Keyword Planner or AnswerThePublic to identify conversational and question-based keywords.
Is voice search optimisation expensive?
Not necessarily. Many voice search optimisation strategies, like improving site speed and creating FAQ pages, are cost-effective.
Start Optimising for Voice Search Today
Voice search is no longer a futuristic concept—it’s here, and it’s growing fast. By implementing these strategies, you can ensure your business stays ahead of the curve.
Ready to take your SEO game to the next level? Contact us at iSonic Media to learn how we can help you dominate voice search and beyond. Discover why we’re the best white-label digital marketing agency in India.
By following these tips and strategies, you’ll be well on your way to mastering voice search optimisation.




